Welcome to the world of Amazon FBA! If you’re new to selling on Amazon, you’ve likely heard terms like “FBA,” “ocean shipping,” and “last-mile delivery” thrown around. They might sound intimidating at first, but don’t worry—I’m here to break it all down for you step by step. By the end of this article, you’ll understand how your products travel from a factory overseas to an Amazon warehouse (via ocean shipping) and then make their final journey to your customers (via last-mile delivery). Plus, we’ll dive deep into the differences between Amazon FBA last-mile truck delivery and UPS delivery—two key players in getting your goods where they need to go.
This guide is designed for Amazon newbies like you—people who are just starting out and want to grasp the logistics behind Fulfillment by Amazon (FBA). Whether you’re sourcing products from China, Europe, or anywhere else, understanding how shipping works is crucial to your success. Let’s get started!
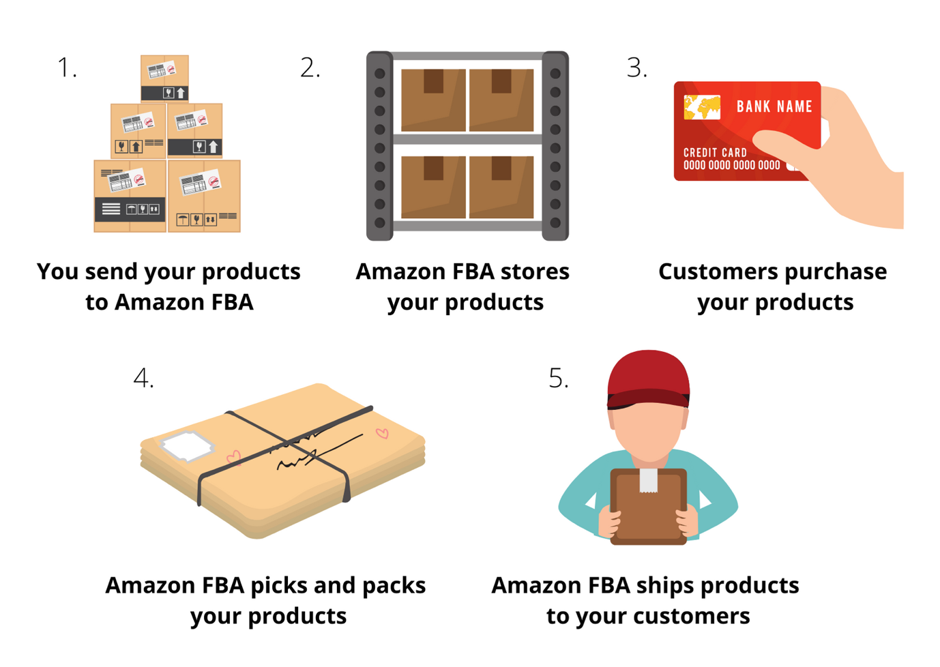
What Is Amazon FBA?
Before we dive into the shipping details, let’s clarify what Amazon FBA is. FBA stands for “Fulfillment by Amazon.” It’s a program where you send your products to Amazon’s warehouses (called fulfillment centers), and Amazon takes care of the rest—storing your inventory, picking and packing orders, shipping them to customers, and even handling returns and customer service. As a newbie, this is a huge relief because it lets you focus on finding great products and growing your business instead of worrying about logistics.
But here’s the catch: you’re responsible for getting your products to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. That’s where ocean shipping and last-mile delivery come in. These are the two main stages of the journey your products take before Amazon steps in to handle customer orders.
Stage 1: Ocean Shipping – Getting Your Products Across the Globe
Most Amazon sellers source their products from countries like China, Vietnam, or India because manufacturing costs are lower there. If you’re starting out, you’re probably doing the same. Since these countries are overseas, the most affordable way to ship large quantities of goods to the United States (or wherever your target market is) is by ocean shipping.
What Is Ocean Shipping?
Ocean shipping means transporting your products across the sea on massive cargo ships. These ships carry thousands of containers filled with goods from sellers like you. It’s slower than air shipping (which uses planes), but it’s much cheaper, especially if you’re shipping a lot of products. For example, shipping a container by sea might cost $3,000-$5,000, while air shipping the same amount could cost $10,000 or more. As a newbie, saving money is key, so ocean shipping is often your best bet.
How Does Ocean Shipping Work for Amazon FBA?
Here’s a simplified breakdown of the process:
- Your Supplier Prepares the Goods: Once you’ve ordered your products, your supplier (like a factory in China) packs them into boxes or pallets and prepares them for shipping.
- Freight Forwarder Steps In: You’ll likely work with a freight forwarder—a company that specializes in arranging international shipping. They handle the paperwork, book space on a cargo ship, and coordinate the journey.
- Goods Load Onto the Ship: Your products are loaded into a container (either a full container or a shared one) and placed on a ship at a port, like Shanghai or Shenzhen.
- The Ocean Journey: The ship sails across the ocean to a port near your target Amazon fulfillment center—say, Los Angeles or New York. This can take 2-6 weeks, depending on the distance and weather.
- Despacho de aduanas: When the ship arrives, your goods go through customs. Your freight forwarder helps with this by submitting documents and paying any import duties or taxes.
- Arrival at the Destination Port: Once cleared, your products are ready to move to the next stage—getting to Amazon’s warehouse.
Full Container Load (FCL) vs. Less Than Container Load (LCL)
When you ship by ocean, you’ll hear about two options: Full Container Load (FCL) and Less Than Container Load (LCL). Here’s what they mean:
- FCL: You rent an entire container (usually 20 or 40 feet long) for your products. This is great if you’re shipping a large quantity because it’s faster (no waiting to share space) and safer (your goods aren’t mixed with others). But it’s more expensive upfront.
- LCL: You share a container with other sellers’ goods, paying only for the space you use. This is cheaper and perfect for newbies with smaller shipments, but it takes longer because the container has to be filled before it ships.
As a beginner, start with LCL if your order is small (like a few boxes). As your business grows, you might switch to FCL to save time and streamline the process.
Why Ocean Shipping Matters to You
Ocean shipping is the backbone of your supply chain. It’s how you get your products from the factory to the U.S. (or your market) affordably. But it’s only half the journey. Once your goods arrive at the port, they need to reach Amazon’s fulfillment centers. That’s where last-mile delivery comes in.
Stage 2: Last-Mile Delivery – Getting to Amazon’s Warehouse
You might think “last-mile delivery” means delivering to your customers’ doorsteps—and it often does. But in the context of Amazon FBA, last-mile delivery refers to the final leg of getting your products from the port to Amazon’s fulfillment centers. This is a critical step because Amazon won’t take over until your goods are safely in their warehouses.
What Is Last-Mile Delivery in FBA?
Last-mile delivery is the process of transporting your goods from the destination port (like Los Angeles) to the specific Amazon fulfillment center where you’ve told Amazon to store your inventory. Amazon assigns you one or more fulfillment centers when you create a shipping plan in Seller Central (your Amazon seller dashboard). For example, they might send your goods to a warehouse in California, Texas, or Pennsylvania.
This stage is called “last-mile” because it’s the final stretch of the journey before Amazon takes ownership. It’s different from customer delivery because it’s about getting your inventory into Amazon’s hands, not your buyers’.
How Does Last-Mile Delivery Work for FBA?
Here’s how it typically goes:
- Unloading at the Port: Your container arrives, and the goods are unloaded. If you used LCL, your boxes are separated from others in the container.
- Preparing for Amazon: Your freight forwarder or a third-party logistics provider (3PL) might palletize your goods (stack them on wooden pallets) and label them according to Amazon’s strict requirements. Amazon has rules about how boxes and pallets must be packed and labeled—don’t skip this step!
- Transportation to the Warehouse: Your goods are loaded onto a truck and driven to the assigned Amazon fulfillment center. This could be a short trip (a few miles) or a longer haul (hundreds of miles), depending on the port and warehouse locations.
- Delivery and Check-In: The truck arrives at the fulfillment center, and Amazon staff unload and check in your inventory. Once checked in, your products are ready to be sold.
Last-Mile Delivery Options for FBA
When it comes to last-mile delivery to Amazon’s warehouses, you have a few methods to choose from. The two most common are Amazon FBA last-mile truck delivery and UPS delivery. Let’s explore each one and then compare them so you can decide what’s best for your business.
Amazon FBA Last-Mile Truck Delivery
What Is It?
Amazon FBA last-mile truck delivery is part of Amazon’s Partnered Carrier Program (PCP). Through this program, Amazon partners with trucking companies to offer discounted shipping rates for sellers sending inventory to fulfillment centers. It’s designed to make the last-mile process smooth and cost-effective for FBA sellers like you.
How It Works
- Create a Shipping Plan: In Seller Central, you tell Amazon what products you’re sending and how many units. Amazon assigns you one or more fulfillment centers.
- Choose a Partnered Carrier: When you finalize your shipping plan, Amazon offers you the option to use their partnered carriers for last-mile delivery. These are trucking companies Amazon has agreements with.
- Book the Shipment: You select the partnered carrier option, and Amazon provides a discounted rate. You print shipping labels and schedule a pickup or drop-off.
- Trucking to the Warehouse: The partnered carrier picks up your goods from the port (or a freight forwarder’s warehouse) and delivers them to the Amazon fulfillment center.
Types of Amazon FBA Truck Delivery
Amazon offers three main truck delivery methods under the Partnered Carrier Program:
- Small Parcel Delivery (SPD): For small shipments (usually less than 150 pounds or a few boxes), Amazon partners with carriers like UPS or FedEx to deliver individual packages. This is great for newbies with small initial orders.
- Menos de camión completo (LTL): For medium-sized shipments (a few pallets but not a full truck), LTL trucks carry your goods along with other sellers’ inventory. It’s cost-effective for shipments between SPD and full truckload.
- Camión completo (FTL): For large shipments (a full truck’s worth), FTL uses a dedicated truck to deliver your goods straight to the fulfillment center. This is faster but more expensive, so it’s better for established sellers.
Pros of Amazon FBA Truck Delivery
- Discounted Rates: Amazon negotiates bulk rates with carriers, so you save money compared to booking a truck yourself.
- Streamlined Process: Everything is managed through Seller Central—labels, tracking, and scheduling are all in one place.
- Reliable Tracking: Amazon provides updates on your shipment’s status, so you know when it arrives.
- Amazon Support: If something goes wrong (like a delay), Amazon’s support team can help since it’s their program.
Cons of Amazon FBA Truck Delivery
- Limited Flexibility: You’re locked into Amazon’s partnered carriers and their schedules. You can’t choose your own trucking company.
- Potential Delays: During busy seasons (like the holidays), fulfillment centers can get backed up, slowing down check-in times.
- Pallet Requirements: For LTL and FTL, your goods must be palletized and labeled perfectly, or Amazon might reject them.
UPS Delivery for Amazon FBA
What Is It?
UPS (United Parcel Service) is one of the biggest shipping companies in the world, and you can use it independently to handle last-mile delivery to Amazon fulfillment centers. Unlike Amazon’s partnered carriers, UPS isn’t tied to the Partnered Carrier Program—you book it directly through UPS or your freight forwarder.
How It Works
- Coordinate with Your Freight Forwarder: After your goods arrive at the port, your freight forwarder arranges UPS delivery to the Amazon fulfillment center.
- Book the Shipment: You or your forwarder schedules a UPS pickup from the port or a warehouse and provides the Amazon warehouse address.
- Labeling and Prep: Your goods are labeled (either by the forwarder or at the factory) to meet Amazon’s FBA requirements.
- Entrega: UPS trucks your goods to the fulfillment center, and you track the shipment using UPS’s system.
Types of UPS Delivery
UPS offers similar options to Amazon’s truck delivery methods:
- Small Parcel Delivery: UPS is famous for delivering small packages (think brown trucks dropping off boxes). This works for small FBA shipments.
- UPS Freight (LTL/FTL): For larger shipments, UPS Freight handles less-than-truckload or full-truckload deliveries to Amazon warehouses.
Pros of UPS Delivery
- Flexibilidad: You’re not tied to Amazon’s program, so you can use UPS whenever and however you want.
- Wide Network: UPS has hubs and trucks everywhere, making it easy to arrange pickups and deliveries.
- Velocidad: UPS often delivers faster than some partnered carriers, especially for small parcels.
- Control: You or your freight forwarder have more say over the process, which can be reassuring as a newbie.
Cons of UPS Delivery
- Mayores costes: Without Amazon’s discounted rates, UPS can be pricier, especially for large shipments.
- More Work: You have to manage the booking, tracking, and coordination yourself (or through a forwarder), unlike the streamlined Partnered Carrier Program.
- No Amazon Integration: UPS shipments don’t automatically update in Seller Central, so you’ll need to keep track separately.
Key Differences Between Amazon FBA Last-Mile Truck Delivery and UPS Delivery
Now that you know how both options work, let’s compare them side by side. As a newbie, understanding these differences will help you choose the right method for your first shipment.
1. Cost
- Amazon FBA Truck Delivery: Cheaper because Amazon negotiates bulk discounts with partnered carriers. For example, shipping a pallet via LTL might cost $100-$150 with a partnered carrier, compared to $200+ with UPS.
- UPS Delivery: More expensive since you’re paying UPS’s standard rates. Small parcels might cost $10-$20 each, while freight shipments can add up quickly.
Winner for Newbies: Amazon FBA truck delivery—saving money is critical when you’re starting out.
2. Ease of Use
- Amazon FBA Truck Delivery: Super easy. You handle everything in Seller Central, from booking to printing labels. It’s designed for beginners.
- UPS Delivery: Requires more effort. You’ll need to work with UPS directly or rely on your freight forwarder to manage it.
Winner for Newbies: Amazon FBA truck delivery—less hassle means less stress.
3. Speed
- Amazon FBA Truck Delivery: Can be slower, especially during peak seasons when fulfillment centers are busy. Check-in delays (after delivery) can take weeks.
- UPS Delivery: Often faster for small parcels, and UPS Freight can be quick for pallets if scheduled well. No reliance on Amazon’s partnered carrier backlog.
Winner for Newbies: UPS—if speed matters more than cost.
4. Flexibility
- Amazon FBA Truck Delivery: Limited to Amazon’s partnered carriers and their schedules. You’re stuck with their options.
- UPS Delivery: More flexible. You can book UPS anytime, anywhere, and adjust based on your needs.
Winner for Newbies: UPS—if you want more control.
5. Tracking and Support
- Amazon FBA Truck Delivery: Tracking is built into Seller Central, and Amazon support can step in if issues arise.
- UPS Delivery: Tracking is through UPS’s system, and you’ll deal with UPS customer service (or your forwarder) for problems—not Amazon.
Winner for Newbies: Amazon FBA truck delivery—integrated tracking and Amazon’s backing are beginner-friendly.
Which Should You Choose as a Newbie?
As an Amazon newbie, your decision depends on your priorities:
- If You Want to Save Money and Keep It Simple: Go with Amazon FBA last-mile truck delivery through the Partnered Carrier Program. It’s affordable and designed for sellers like you who are just starting out.
- If You Need Speed or Flexibility: Choose UPS delivery, especially if you’re shipping a small batch and want it to arrive quickly, or if you prefer managing the process yourself.
For your first shipment, I recommend starting with Amazon’s Partnered Carrier Program (likely using SPD for small boxes). It’s the easiest and cheapest way to get your feet wet. As you grow, you can experiment with UPS or other options to see what fits your business best.
Tips for a Smooth FBA Shipping Experience
No matter which last-mile method you choose, here are some beginner-friendly tips to avoid headaches:
- Trabajar con un transitario: They’ll handle ocean shipping and can coordinate last-mile delivery, saving you time and stress.
- Follow Amazon’s Rules: Label your boxes and pallets exactly as Amazon requires, or they’ll reject your shipment.
- Planificar con antelación: Ocean shipping takes weeks, and last-mile delivery can face delays. Give yourself a buffer so your inventory doesn’t run out.
- Track Everything: Use Seller Central (for partnered carriers) or UPS’s tracking to monitor your shipment’s progress.
- Empezar poco a poco: Test the process with a small LCL shipment before committing to a full container.
Conclusión
Amazon FBA is an incredible opportunity for newbies to build a business without drowning in logistics—but you still need to master the shipping process. Ocean shipping gets your products across the globe affordably, while last-mile delivery ensures they reach Amazon’s warehouses. Whether you choose Amazon FBA last-mile truck delivery (with its cost savings and simplicity) or UPS delivery (with its speed and flexibility), you’re now equipped to make an informed decision.
As you embark on your Amazon journey, don’t be afraid to ask questions—reach out to your freight forwarder, Amazon Seller Support, or even other sellers in forums. Shipping might seem overwhelming at first, but with each shipment, you’ll gain confidence and expertise. Soon, you’ll be a pro at getting your products from the factory to your customers’ hands. Happy selling!