In the shipping and logistics industry, fluctuating fuel prices can significantly affect overall shipping costs. For business owners involved in regular imports and exports, understanding the Bunker Adjustment Factor (BOC) – a fuel surcharge applied by shipping companies to manage these price variations – is crucial. In this article, we’ll cover how BOC is calculated, how it impacts different types of cargo, and provide strategies for effectively managing BOC charges to maintain stable logistics budgets.
What is BOC in Shipping?
The Bunker Adjustment Factor (BOC), or Bunker Surcharge, is a fee that shipping companies add to base freight rates to counterbalance the changing cost of fuel. BOC charges allow carriers to stabilize their income by passing some of the fuel cost volatility onto shippers. For business owners, a solid understanding of BOC is essential to accurately predict total shipping costs and effectively manage logistics expenses.
Understanding the Calculation of BOC
BOC calculation varies across shipping companies, but the essential factors include the current fuel price per metric ton, vessel capacityet le distance of travel. Below is a breakdown of how these components influence BOC.
Key Factors in BOC Calculation:
- Fuel Price Per Metric Ton:
- The price of bunker fuel (the fuel used by shipping vessels) fluctuates based on global oil market conditions.
- Vessel Size and Capacity:
- Larger vessels consume more fuel but may distribute costs more effectively across high cargo volumes.
- Voyage Distance:
- Longer voyages incur higher fuel consumption, leading to a higher BOC.
Let’s look at a simplified example calculation to clarify.
Exemple de calcul :
Consider a cargo shipment traveling from New York to Hamburg on a vessel consuming 100 metric tons of fuel daily over a 10-day trip. If the bunker fuel price is $600 per metric ton, the total fuel cost for this journey would be:
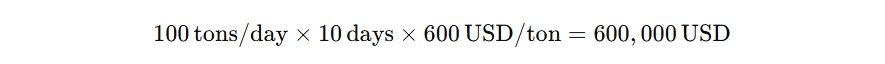
If the shipping line distributes this fuel cost across 5,000 containers, each container would incur a BOC of:
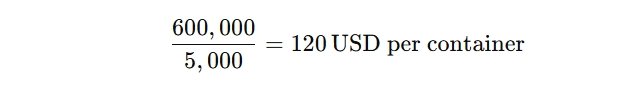
Shipping companies may adjust the BOC according to market trends, recalculating it regularly. By understanding this calculation, business owners can forecast when BOC rates are likely to rise or fall based on fuel price trends and planned routes.
Impact of BOC on Different Types of Cargo
BOC does not impact all types of cargo equally. The cost distribution and sensitivity to fuel surcharges vary depending on cargo type and its shipping requirements.
1. Bulk Cargo:
- Bulk shipments, like coal or grain, are typically shipped in large volumes, making fuel costs a significant portion of the total expense. BOC charges may have a substantial effect on overall costs, especially for long-haul routes.
2. Containerized Cargo:
- For containerized cargo, BOC is usually spread across individual containers, which allows for more cost control. However, container shippers are still affected by BOC adjustments, especially when fuel prices spike unexpectedly.
3. Refrigerated (Reefer) Cargo:
- Temperature-sensitive goods require continuous power to maintain specific temperatures. Reefer containers consume additional fuel to operate, which can increase BOC. This is particularly impactful for goods like pharmaceuticals or perishables, where the price increase can directly influence profitability.
4. High-Value or Fragile Goods:
- Goods with high value or sensitivity to handling may require special transport, incurring higher BOC charges due to added weight, security, or fuel consumption needs. Shippers of such goods often negotiate BOC terms more stringently to avoid substantial fees.
Strategies for Managing BOC Charges
For business owners who frequently ship goods, there are several strategies to manage and potentially mitigate BOC costs.
1. Budgeting for BOC in Logistics Planning:
- Create a buffer in shipping budgets to accommodate potential BOC increases. Reviewing historical BOC charges and monitoring fuel trends can provide a baseline for estimating BOC costs.
2. Negotiating Long-Term Contracts:
- In high-volume shipping scenarios, negotiating contracts with stable BOC rates or capped surcharges can be advantageous. Some carriers offer fixed-rate BOC contracts to large customers, which can provide predictable costs over time.
3. Consolidation des envois:
- By consolidating shipments and optimizing container usage, companies can spread the BOC charge across more products, effectively lowering the surcharge per unit. Additionally, shipping fewer containers less frequently can help control costs.
4. Monitoring Fuel Price Trends:
- Business owners can track global oil prices to anticipate BOC changes. This can inform decisions about when to ship goods, potentially avoiding periods of high fuel costs. Online tools and market reports are available to help monitor these trends.
5. Partnering with Logistics Providers:
- Collaborate with logistics companies or freight forwarders who have established relationships with carriers. They often have negotiated BOC terms that may be more favorable than independent contracts.
6. Optimizing Shipping Routes:
- Choose routes with shorter transit times when possible, as these reduce fuel consumption. Although route flexibility is limited in international shipping, it’s worth exploring alternative ports or routes if they lower BOC costs.
7. Investing in Sustainability:
- Some companies offset fuel costs by investing in more fuel-efficient packaging and loading methods. Reducing overall cargo weight or volume can directly lower fuel requirements, thus minimizing BOC. Moreover, eco-friendly practices may lead to partnerships with carriers focused on green shipping, which could offer lower BOC rates.
Résumé
In today’s volatile fuel market, understanding and managing BOC is crucial for business owners involved in shipping. Knowing how BOC is calculated, how it impacts different types of cargo, and strategies to mitigate these charges can provide a competitive advantage in logistics planning. By implementing effective strategies, such as negotiating BOC rates, consolidating shipments, and monitoring fuel trends, business owners can maintain control over shipping costs and improve the financial stability of their operations.